Ever since the vaccination process has opened for the Indian citizens in the age bracket 18 to 44 years, there has been a mad rush among people to find an available slot on the CoWIN application – India’s indigenous vaccination management platform. The attempts to book a slot have mostly gone in vain as the slots get “Fully Booked” as soon as they are released on the site. Moreover, the frequent CoWIN application issues have compounded the problems further, and people feel they are left in the lurch.
Before we delve into the topic further and see how blockchain can help in resolving the issues, we need to first understand the details about the CoWIN digital platform.
What is CoWIN?
CoWIN is a cloud-based application developed by the Government of India (GOI) for the Covid-19 vaccination drive in the country. Beneficiaries looking for vaccines can register on the CoWIN site by uploading a valid photo identity proof document. The CoWIN application also has the provision for the creation of Department Users (admins and supervisors) and implementing the inoculation process.
What is the Technology Behind CoWIN?
CoWIN, short for COVID Vaccine Intelligence Network is an extension of India’s indigenous system called the Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN) system. The eVIN was introduced by GOI in collaboration with GAVI in 2015. The purpose of eVIN was to enable the real-time visibility of vaccines provided to the states for different diseases and check the temperature across various cold chain facilities across the country. The idea behind eVIN was to make vaccine utilization more efficient, avoid stock-out events and reduce wastage.
- The eVIN system has been repurposed to develop the CoWIN application in collaboration with GAVI and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- UNDP in turn has partnered with Mumbai-based IT company Trigyn to develop CoWIN.
- For cloud services, Amazon Webservices has been chosen over National Informatics Centre’s (NIC) MeghRaj cloud platform.
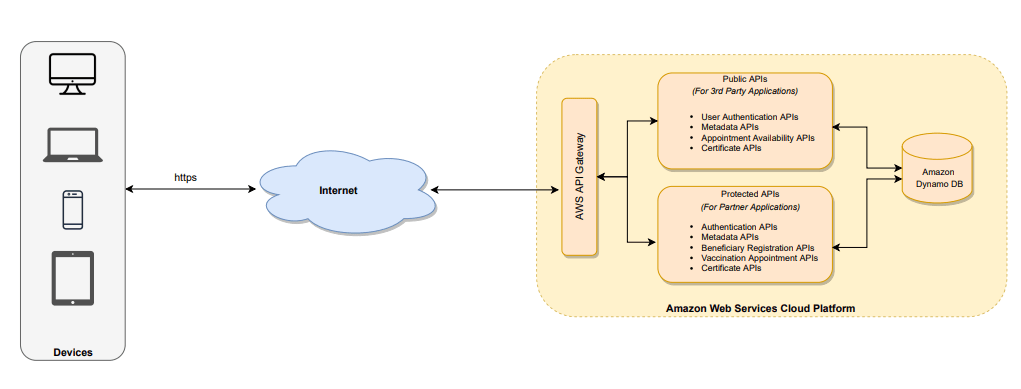
Following is a very high-level illustrative representation of CoWIN architecture. The actual implementation may be different and may have more components.
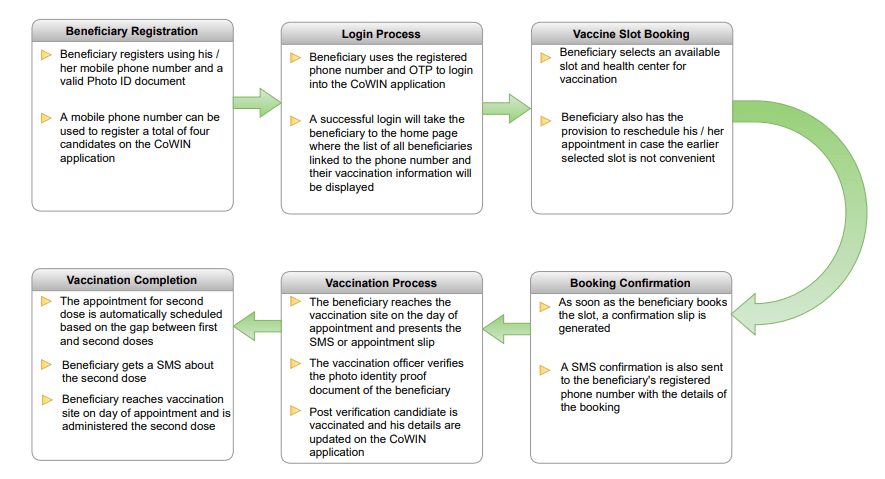
How does the Beneficiary Registration process work on CoWIN Application?
The CoWIN application has various modules. One of the most important modules is the “Beneficiary Registration” module that is aimed at registering for a vaccination session, finding a nearby vaccination center, booking a slot as per availability, and rescheduling an appointment in case the slot or vaccination location is not convenient for the beneficiary. The workflow of beneficiary registration and vaccination process is as follows:
What are the problems with CoWIN Application?
- Reports About Data Manipulation and Fraudulent Bookings
There are many allegations of data manipulation and fraudulent bookings related to the slots. As per one such report, influential people in some areas have been getting their near and dear ones vaccinated in health centers sans the booking on the CoWIN platform. The health care centers are said to be manipulating the data and uploading only “Fully Booked” slots. The Government has taken note of such allegations and investigations are on.
2. Gap in the number of Doses Manufactured and Doses Administered
As per a recent report in a popular Indian tabloid, the number of doses manufactured in production facilities of the vaccine companies is far greater than the number of doses administered. Despite the surplus availability of vaccines, many states have been reporting a shortage of doses and citizens are complaining about the unavailability of slots. This has raised a lot of questions about the entire vaccination management process.
3. Menace of Automation BOTs
The availability of the CoWIN Public APIs has led to competition among the techies in developing BOTs or automated programs/scripts that look for the availability of slots. Showcasing their technical prowess, some even have gone ahead and developed BOTs to book slots automatically as soon as those are available without requiring any manual intervention. There are many such scripts available on the GITHUB repository which helps in booking slots on the CoWIN application. The result is that the poor, the elderly and the not so tech-savvy people have been kept at bay from booking slots. These unethical ways of booking slots are increasing the digital divide among people and leading to a lot of frustration.
4. Technical Glitches
CoWIN has been plagued with technical glitches. Take, for instance, the day when registration was opened for citizens in the age bracket of 18 to 44 years, there was huge web traffic on the CoWIN site and the application crashed. It is said that the Government and the technical team had taken all steps to ensure a smooth registration, yet the web traffic was much more than anticipated which led to the Elastic Load Balancers (ELB) to crash. The issue was quickly fixed and the site was up and running in few hours. However intermittent technical glitches related to the delay in getting OTP are still being encountered.
5. Privacy Policy
The CoWIN application as such does not have any specific policy about how beneficiary data is collected, where it is stored, and how it is accessed. An RTI request about protecting the personal data of beneficiaries on the portal led the Ministry of Health and Welfare to respond that the application’s policy cannot be revealed. The beneficiary data is accessible only to the administrators at the Centre, State, and District levels and not by the common public.
What is Blockchain?
Most people from a technology background are aware of the term Blockchain. It is perhaps one of the biggest tech buzzwords of recent times. However, for the uninitiated, Blockchain in its simplest term means a list of records maintained in a digital ledger stored over a peer-to-peer network. These records are called blocks and each block is linked to its previous record or block using a cryptographic hash thus forming a chain. Apart from the cryptographic hash value, a block also comprises the timestamp and the transactional data. All the nodes (computer) in a blockchain network carry a copy of the digital ledger. Whenever a new transaction is made, the network participants validate the transaction using complex algorithms. Once the transaction is verified, it gets appended to the list of other verified transactions as a new block and gets copied to all the nodes in the blockchain network. Blockchain technology is decentralized and highly transparent. All participants in a blockchain network can view the entire chain. Data manipulation is virtually impossible as the information is timestamped and any attempt to tamper with data will require all the copies of the blockchain to be altered simultaneously.
How Blockchain can address CoWIN Issues?
- Proper Vaccination Management
Blockchain can help in tracking vaccines right from the point it is manufactured in the production facility to the point where the beneficiary receives it. Timestamp information can be entered for the vaccines at each phase on the blockchain so that data cannot be tampered with by anyone. The agencies can also track the number of vaccine doses manufactured as well as the number of doses administered. The beneficiary can also access the information about vaccine storage to see if the dose he is going to receive, has been safely handled.
2. Streamlined Vaccination Process
Blockchain can streamline the current process for registration of beneficiaries, booking of the slots, and ensuring a smooth vaccination at the health care centers. The process can be made full proof to a large extent without any kind of manual intervention. Following is an indicative approach of using blockchain technology in conjunction with the CoWIN platform.
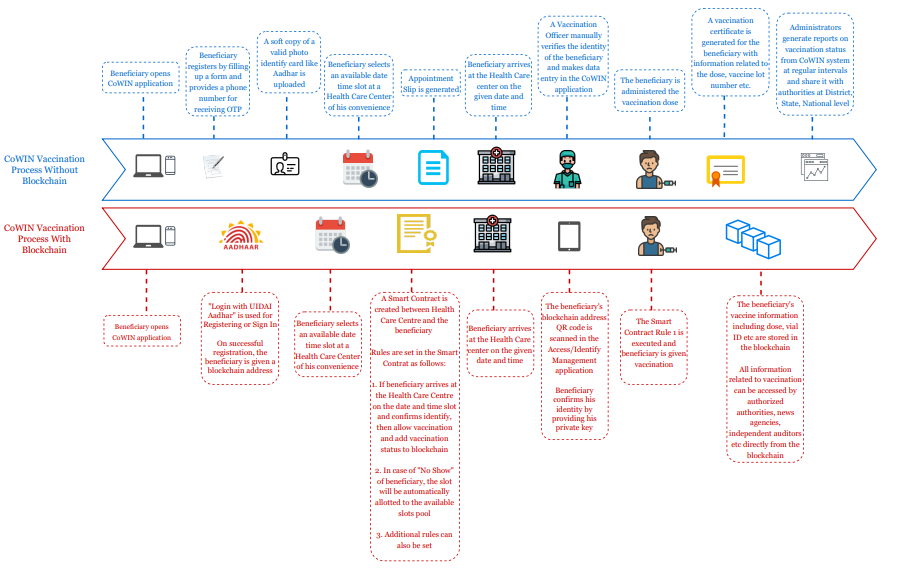
3. Defeating Automation BOTs
One of the most frustrating experiences of trying to book a slot is the problem of automation BOTs. These BOTs are automated scripts that constantly keep pinging the public APIs of the CoWIN platform for the availability of slots. This, in turn, makes the server slow and at times it results in the delay in getting OTPs. Some of the BOTs are programmed to book the slots as soon as they become available bypassing the CoWIN captcha verification. Such programs create a very bad experience for the genuine beneficiaries who try to book the slots on the CoWIN application and in the end are left frustrated. There are ample videos on many video-sharing platforms that show how to use these automated programs to book slots in the blink of an eye. To defeat such BOTs, blockchain coupled with data science/machine learning technologies can be used. Provisions like recognizing legitimate clicks or scroll behavior on the page as well as prompting the users to enter their private keys to confirm their identity on the CoWIN application before booking an available slot can help in addressing the BOT issues.
4. Data Privacy
The blocks in a blockchain are secured through cryptography. The participants in a blockchain can access the information only using their private keys. Since the blocks are stored in a decentralized manner on various nodes and not on a central system, there is no single point of failure. It is extremely difficult for hackers to tamper with the blocks on each node that is part of the blockchain.
Is Blockchain a Magic Wand?
Blockchain has a lot of potential but it is not the solution to every problem. It has its share of issues too.
1. Problem with Adoption
Though the concept of Blockchain has been known for quite some time now, yet there has been no major implementation of this technology except for cryptocurrencies. In fact, cryptocurrencies are responsible for the negative reputation of blockchain because of which people do not have enough trust in the technology.
2. Problem with Adoption
In a country like India, there is a large digital divide. A lot of people still do not have access to the Internet or modern technologies. There are network connectivity issues in many places too. Under such circumstances, an application built on blockchain technology may not have many takers.
3. Issues with Scalability
One of the main issues with blockchain technology is it is not scalable. As the blockchain grows, scalability gets impacted. The legacy technologies on the other hand are scalable, often handling thousands of transactions per second. In comparison, blockchain technology can handle very few transactions per second, for example, Bitcoin can handle only 4.6 transactions per second.
4. Incompatibility with Legacy Systems
Blockchain applications do not interface well with legacy systems. Hence to implement such technologies, a complete overhaul of the infrastructure and systems will be needed.
Conclusion
The idea of using blockchain technology on the CoWIN platform depicted above is purely conceptual. The real implementation of blockchain technology is easier said than done. However, blockchain technology has a lot of potential. In fact, two hospitals in the UK have already implemented a vaccine monitoring system using blockchain technology.
Many companies like IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have started investing in blockchain solutions. The future is progressive, and the world is moving towards an era where blockchain-powered solutions will become commonplace in almost all fields.
Disclaimer: Most of the information in this article about CoWIN’s current state has been taken from the details already available in the public domain. The idea behind the post is to see if any solution can be devised by leveraging the options provided by the current breed of technologies to make India’s vaccination process streamlined, foolproof and transparent.
For more posts on technology, you may visit the section Tech Bytes
For posts on travel, you may visit the section Wander Lust